Epigenetic Fingerprints Link Early-Onset Colon and Rectal Cancer to Pesticide Exposure.
Silvana CE Maas, Iosune Baraibar, Odei Blanco-Irazuegui, Josep Tabernero, Elena Elez, Jose A. Seoane
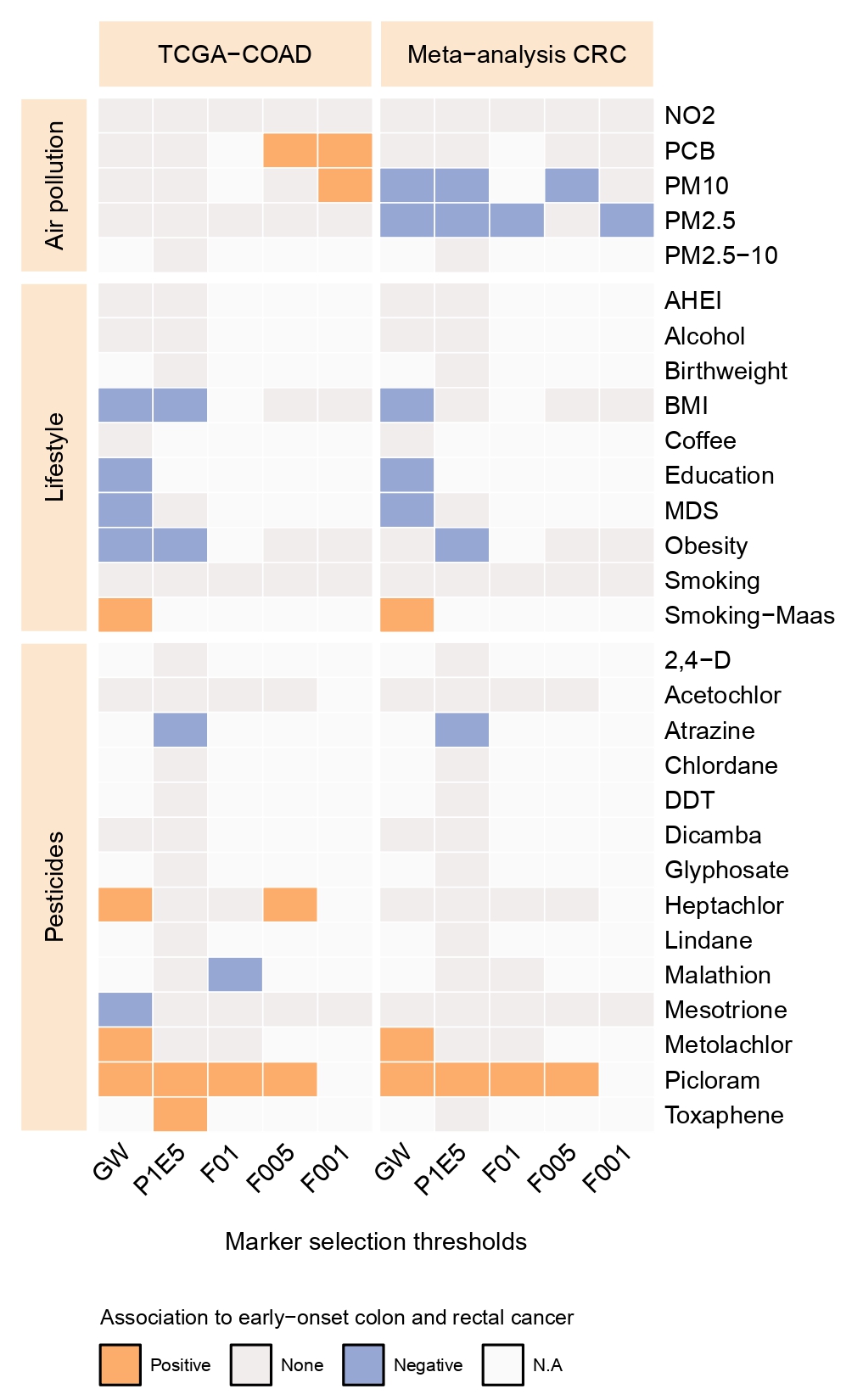
The incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) is rapidly rising in individuals younger than 50, particularly in high-income countries. This rise parallels shifts in lifestyle and environmental factors, collectively termed the exposome; however, whether these are causally linked to the development of early-onset CRC (EOCRC) has not been investigated. Due to limited exposome data in most cancer cohorts, we constructed weighted methylation risk scores (MRS) as proxies for exposome exposure to pinpoint specific risk factors associated with EOCRC. Our analysis confirms previously identified risk factors, such as educational attainment, diet, and smoking habits. Moreover, we identified the exposure to the herbicide picloram as a novel risk factor (Padj. = 0.00049), a result we replicated in a meta-analysis comprising six CRC cohorts (P = 0.021), comparing EOCRC cases with patients diagnosed aged ≥70. Subsequently, we employed population-based data from 81 U.S. counties over 20 years and validated the association between picloram usage and EOCRC incidence (P = 2.87×10-3). These findings highlight the critical role of the exposome in EOCRC risk, underscoring the urgency for targeted personal and policy-level interventions.